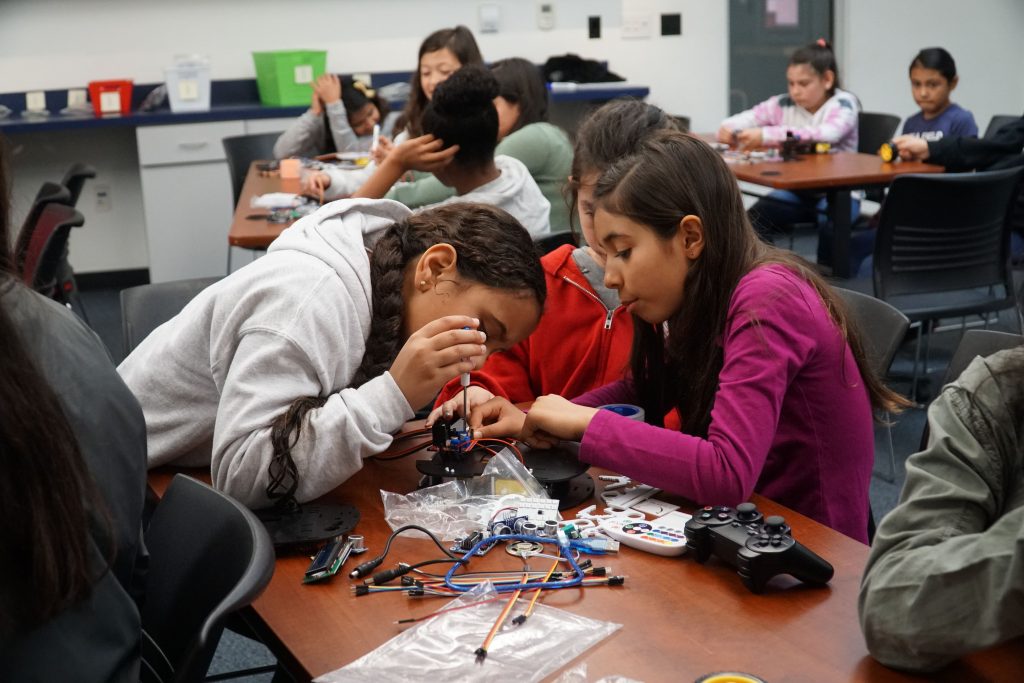
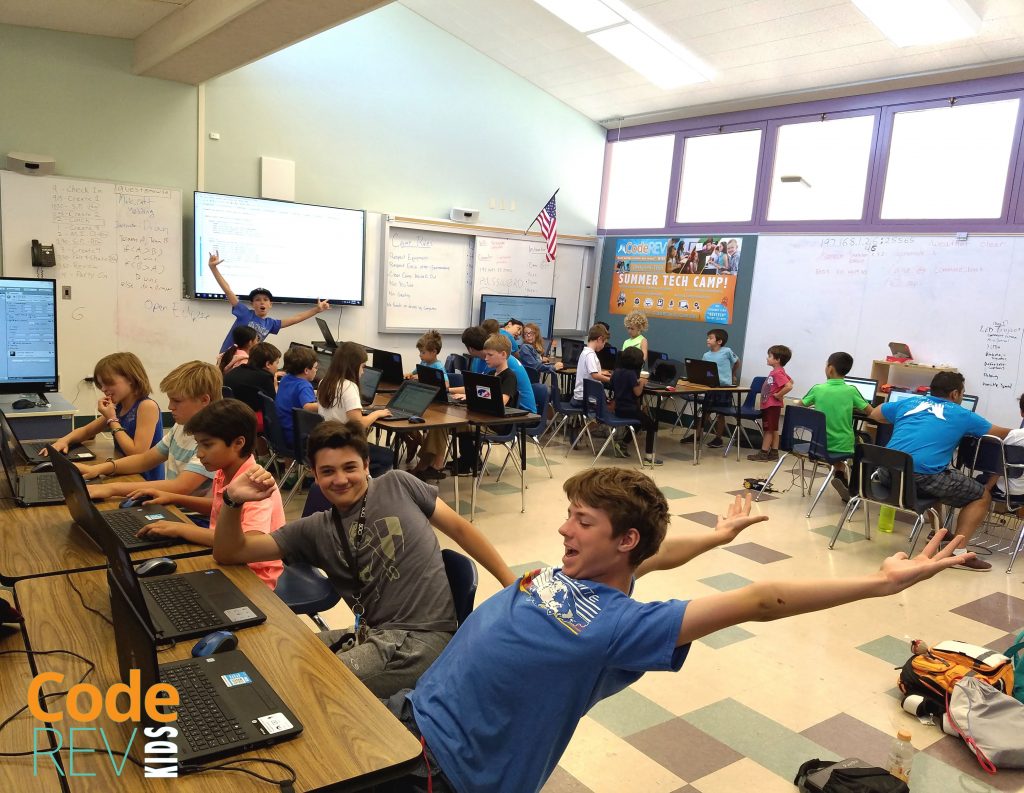
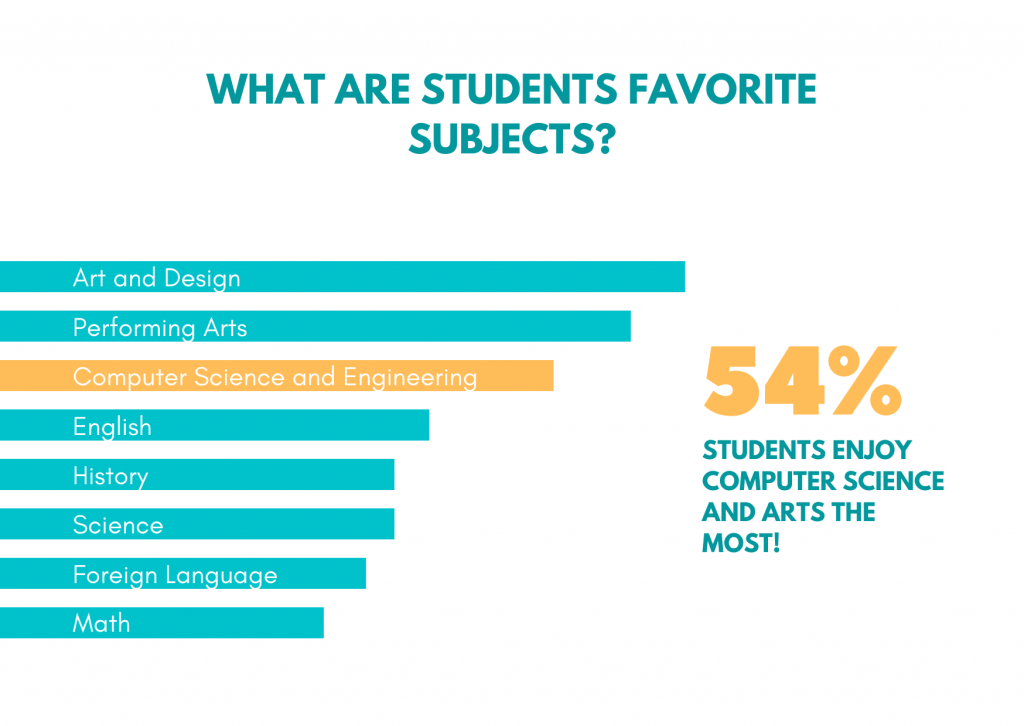
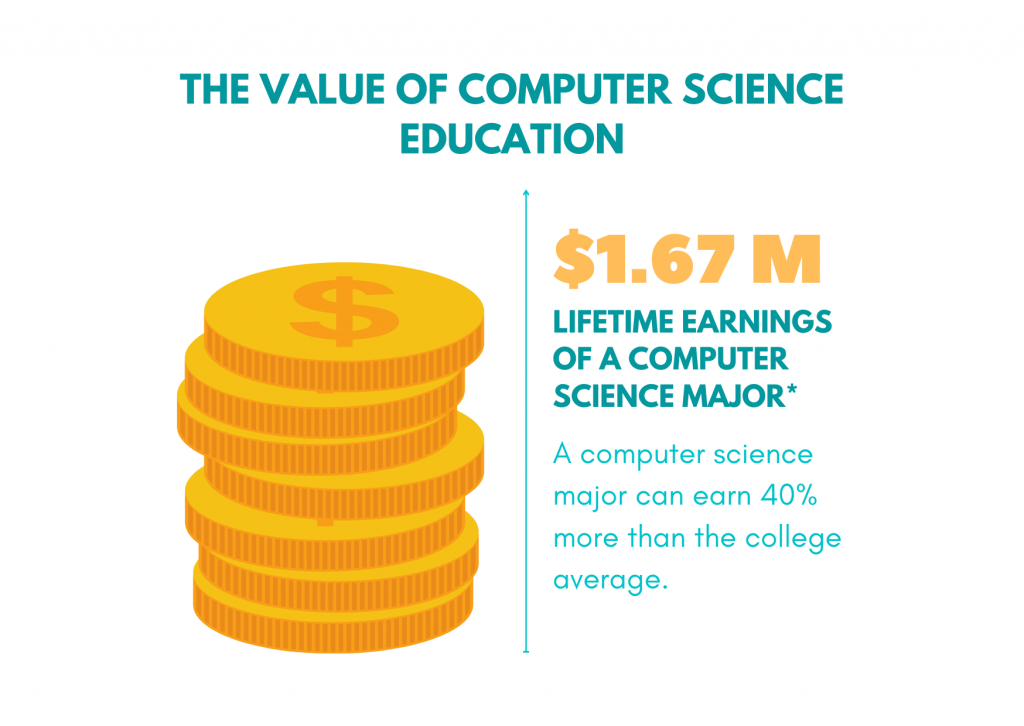
Summer is just around the corner, and many parents are looking for fun and enriching activities for their kids. If you’re a parent looking for something that will not only keep your child engaged but also unlock his or her future potential, here are some key points you should consider before choosing a Summer STEM Camp for your child this summer.
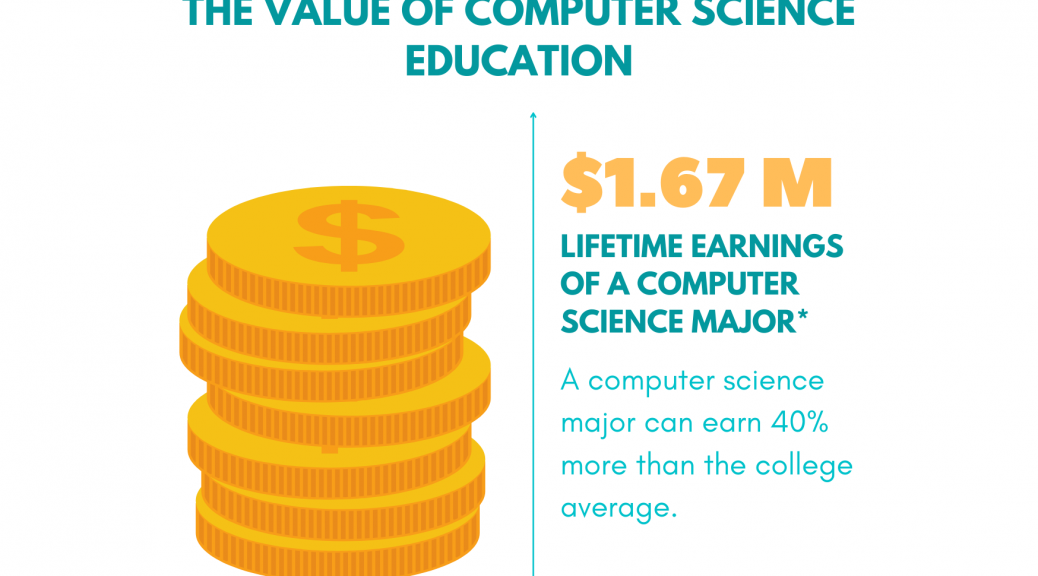
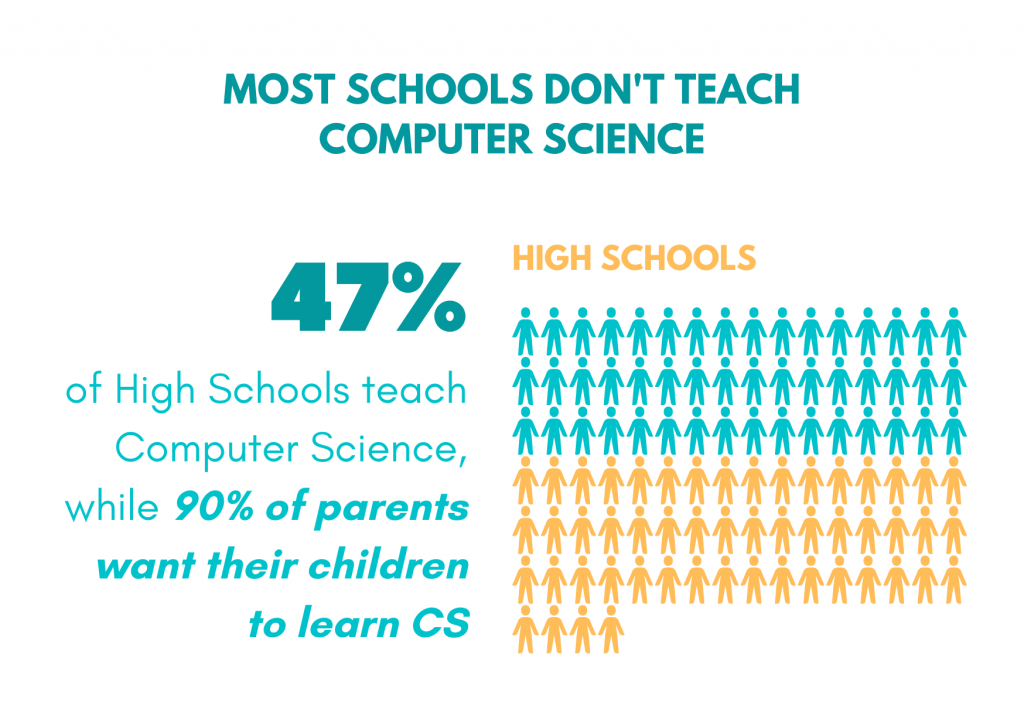
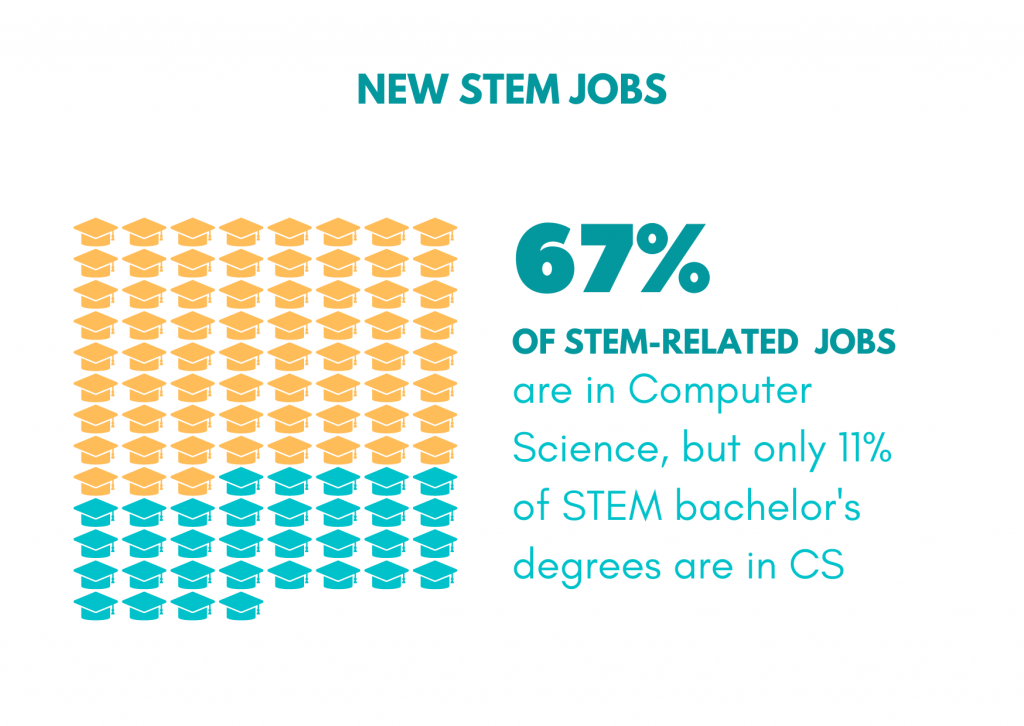
STEM stands for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math, and it encompasses a wide range of fields and skills that are critical to success in the 21st century. STEM education is becoming increasingly important as technology advances and the job market shifts towards more STEM-based careers. By enrolling your child in a summer STEM camp, you can give them a head start on developing the skills they will need to thrive in the future.
What are the benefits of Summer STEM Camps?
Summer STEM camps provide numerous benefits for children of all ages. Here are just a few:
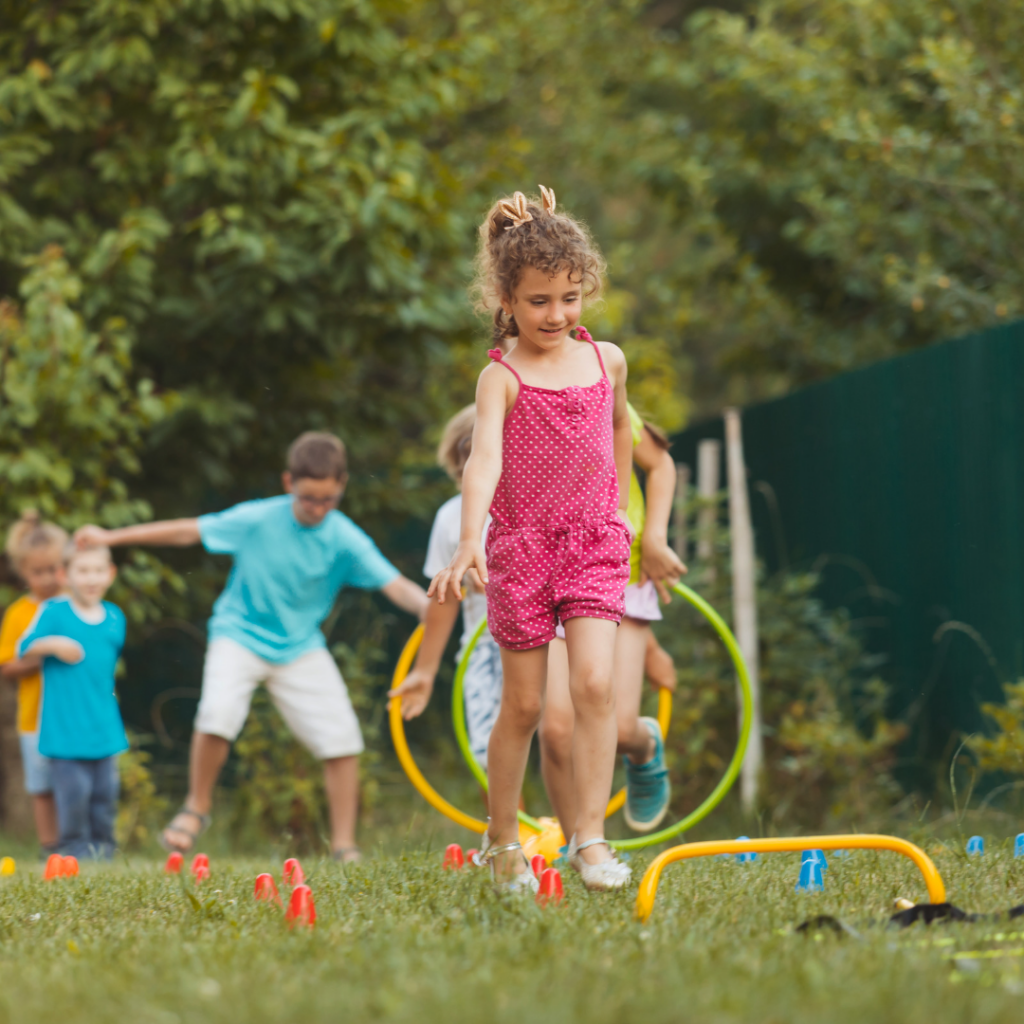

- Hands-on learning opportunities: STEM education is all about learning through doing. Summer STEM camps provide children with the chance to work on real-world projects, conduct experiments, and solve problems in a hands-on and interactive environment.
- Boosting critical thinking and problem-solving skills: STEM education done correctly requires children to think critically and solve complex problems. By participating in a summer STEM camp, children can develop their analytical and problem-solving skills, which will be valuable in all aspects of their lives.
- Teamwork and communication skills: STEM projects often require teamwork and collaboration. By working with other children in a summer STEM camp, children will learn how to communicate effectively, work as part of a team, and build leadership skills.
- Inspires creativity and innovation: STEM education encourages children to be creative and innovative. By participating in a summer STEM camp, children will be exposed to new ideas and technologies that will inspire their curiosity and creativity.
How to Choose the Right Summer STEM Camp for Your Child?
Choosing the right summer STEM camp for your child can be a daunting task. Here are some factors to consider when making your decision:
- Consider your child’s interests: Does your child have a particular interest in science, technology, engineering, or math? Look for a summer STEM camp that aligns with their interests and passions. Are they into tech, hands-on activities, roller coasters, legos, robots, making games, etc? Are arts and design involved in some ways?
- Age range and skill level: Make sure the camp is appropriate for your child’s age and skill level. Some camps are geared towards younger children, while others are more advanced and/or cater to older children with a higher level of knowledge and experience.
- Safety and supervision: Ensure that the camp has proper safety measures in place and that there are qualified instructors and counselors supervising the children. Look for camps that have good/great ratings by the public, are accredited, or have a good safety record.
- Location and transportation: Consider the camp’s location and whether transportation is provided or if you’ll need to arrange for transportation yourself. Make sure the camp’s location is convenient for you and your child.
Summer STEM camps are a fantastic option for parents looking to provide their children with an engaging and educational summer experience. Explore hands-on learning opportunities, build critical thinking and problem-solving skills, encourage teamwork and communication, and inspire creativity and innovation.
By choosing the right summer STEM camp for your child, you can give them a head start on developing the skills they need to succeed in the future. Go ahead and check out our multiple camp locations and see if there’s one that’s right for your child. You never know, it could be the start of an exciting journey towards a bright and rewarding future in STEM and innovation!